Security System Analyzer
A complete report and diagnosis is delivered. - Interactive version of the report fully queryable with filters.- Diagnosis and actions to take if required.
Security Audit Journal Analyzer
Security System Guard
Rules based (over 30 parameters per rule) and association rules based.
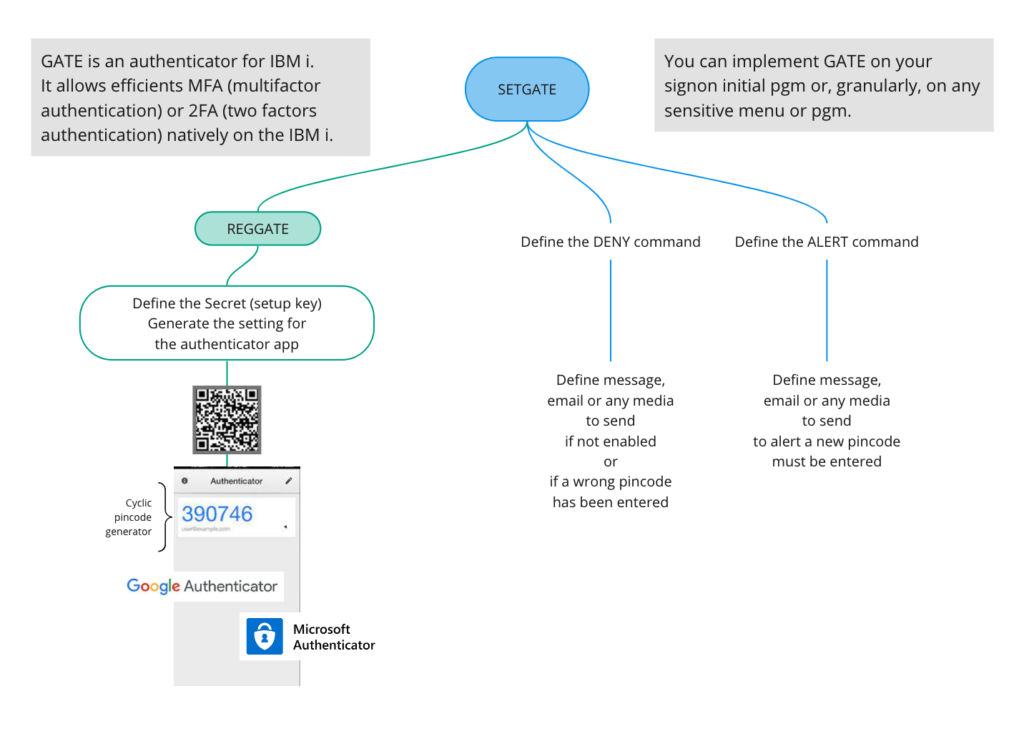
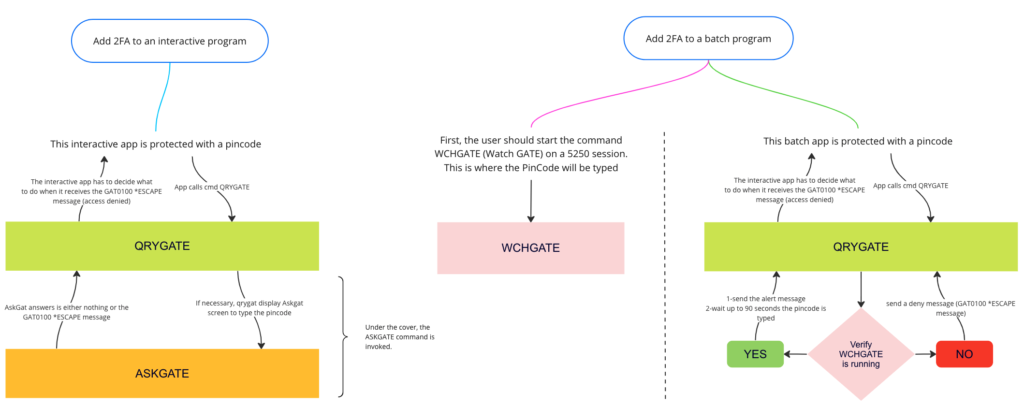
MFA/2FA IBM i Authenticator GATE
Add a 2nd factor authentication at the signon level or at any specific menus or sensitive programs. Native IBM i implementation (no other servers required).
CONTACT US
Get in Touch!
FAQ
In term of cyber security is the IBM i secure?
IBM i, formerly known as AS/400, is known for its robust security features. However, like any system, the security of IBM i depends on various factors, including configuration, management practices, and the implementation of additional security measures. It’s important to ensure that the system is regularly updated with security patches, standards are followed, and access controls are appropriately configured to minimize potential vulnerabilities. Ultimately, no system can be considered completely immune to cyber threats. It’s essential to maintain a proactive approach to security by regularly reviewing and updating security measures based on industry best practices and emerging threats.
What are the primary steps to consider for the IBM i security?
To improve the cyber security of an IBM i system, here are some primary steps to consider:
- Regularly apply system updates and patches: Keep the IBM i system up to date with the latest fixes and updates provided by IBM. This includes both operating system updates and firmware updates for hardware components.
- Implement strong access controls: Define user profiles with appropriate levels of access. Use the principle of least privilege, granting users only the access they need to perform their job responsibilities. Regularly review user accounts and remove unnecessary privileges.
- Enable and configure security features: Take advantage of the built-in security features provided by IBM i, such as object-level security, SSL/TLS encryption, authorization lists, auditing, and strong password policies. Configure these features according to your security requirements.
- Implement network security measures: Ensure that network connections to the IBM i system are properly secured. Use firewalls to restrict access and configure network protocols to use secure and encrypted communication channels.
- Regularly monitor system activity: Set up system monitoring tools that can detect and alert you to unusual or suspicious activity. Monitor system logs, audit journals, and network traffic to identify potential security incidents or policy violations.
- Educate users and promote security awareness: Train system users on security best practices, such as creating strong passwords, avoiding suspicious links or attachments, and being cautious with system privileges. Regularly reinforce security awareness through training programs or communication channels.
- Conduct regular security audits: Perform periodic security assessments and penetration tests to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses. Engage a qualified security professional or team to review your system’s configuration, policies, and controls. Remember, cyber security is an ongoing process. Regularly reassess and update your security measures to address emerging threats and evolving security best practices.
What is the risk of a cyber threat?
The risk of cyber threats to IBM i systems can vary depending on several factors. Here are some potential risks to consider:
- Unauthorized access: If proper security measures are not in place, cybercriminals may gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, applications, or system resources on IBM i.
- Data breaches: Cyber threats may lead to data breaches, where sensitive information stored on IBM i systems is accessed, stolen, or exposed, potentially leading to financial loss, reputational damage, or legal issues.
- Malware attacks: IBM i systems can be vulnerable to malware, including viruses, worms, ransomware, or Trojans, which could disrupt operations, compromise data integrity, or cause system failures.
- Insider threats: Insider threats, such as unauthorized or malicious actions by employees or trusted individuals, can pose a risk to IBM i security. These threats may involve unauthorized data access, tampering, or misuse of privileges.
- Network vulnerabilities: Weak network security controls or misconfigurations can expose IBM i systems to potential cyber threats. Attackers may exploit network vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access or launch attacks on connected systems.
- Lack of patch management: Failure to promptly apply software updates and security patches may leave IBM i systems vulnerable to known exploits and cyber attacks. Regular patch management is crucial to mitigate risks.
- Social engineering attacks: Cybercriminals may attempt to deceive users through social engineering techniques like phishing or impersonation, aiming to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information or providing unauthorized system access.
To mitigate these risks, organizations should implement robust security measures, including access controls, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, regular security audits, employee training, and incident response plans.
Are there any cases of ransomware for the IBM i ?
Yes, there have been reported cases of ransomware affecting IBM i systems. While IBM i has historically been considered a more secure platform, it is not immune to ransomware attacks. Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts files or locks users out of their systems, demanding a ransom payment to restore access. Ransomware attacks on IBM i systems often stem from various sources, including:
- Phishing emails: Attackers may use phishing techniques to trick users into clicking on malicious links or opening infected attachments, leading to the installation of ransomware on the system.
- Exploiting vulnerabilities: If IBM i systems are not kept up to date with patches and security updates, they may be vulnerable to exploits that allow attackers to gain unauthorized access and deploy ransomware.
- Social engineering: Cybercriminals may attempt to exploit human vulnerabilities through social engineering, tricking individuals into providing access credentials or cooperating in installing ransomware.
IBM i systems can be protected against ransomware attacks by implementing industry-standard security practices, such as:
- Regular system updates: Keeping the system up to date with the latest patches and security updates is crucial in mitigating vulnerabilities that attackers may exploit.
- Access controls: Implementing strong access controls and user authentication mechanisms can help prevent unauthorized access to the system by potential attackers.
- Backup solutions: Regularly backing up critical data and storing it offline or in a secure location helps mitigate the impact of ransomware attacks, enabling the recovery of data without paying a ransom.
- Employee education and awareness: Training employees about the risks of ransomware, phishing, and social engineering can help reduce the likelihood of successful attacks.
- Security monitoring and incident response: Implementing security monitoring tools and an incident response plan can help detect and respond to ransomware attacks promptly.
Remember that no system or measure can provide 100% guarantee against ransomware attacks. It’s important to stay vigilant, maintain security best practices, and regularly review and update security measures.
Does an organization's breach can lead to a price increase for customers?
According to a 2022 report from IBM 60% of organizations’ breaches led to increases in prices passed on to customers. Full report here: https://www.ibm.com/reports/data-breach

