Fully integrated evolving development environment for the IBM i platform.
Not a given set of tools, but a fully integrated development environment designed for the users and with the users. You’ll benefit most from an open development of the editor. If you’re looking for an alternative to your old green screen editor, you don’t need to search further.
Since 1992, Remain Software empowers its customers worldwide with robust, reliable and flexible solutions and support for their evolving needs. MiWorkplace has been the most recent addition to our porftolio of change-management, workflow, DevOps and end-to-end ALM solutions. And we’re planning to make it even greater with the release of new versions like V1.25.0

MiWorkplace currently has two options to choose as language: English and German, and you’ll be able to choose from multiple themes. It’s also multi-patform, suitable for Linux, Windows or Mac. It’s really easy to install, and you can head to our Youtube list of MiWorkplace videos and tutorials to quickly learn how to do it. It is lightweight and no software installation or server is required, so what are you waiting for to try it?
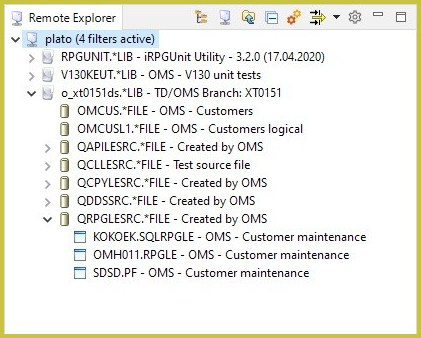
Remote Explorer
The Remote Explorer is the heart and starting point of the application. In the Remote Explorer, the connections to the IBM i servers are managed and the QSYS and root file system in the IFS can be browsed. The libraries, source, and stream files can be managed from it. And all actions like create, delete, rename, copy, paste, and more, are supported.
The toolbar at the top enables several actions. You can easily create and name new connections, which are the starting point for working with the IBM i server. Opening the filter editor, you can activate and de-activate filters. And it includes Filesystem, Go Up, Collapse all, Open the License Editor, and Preferences actions, too.
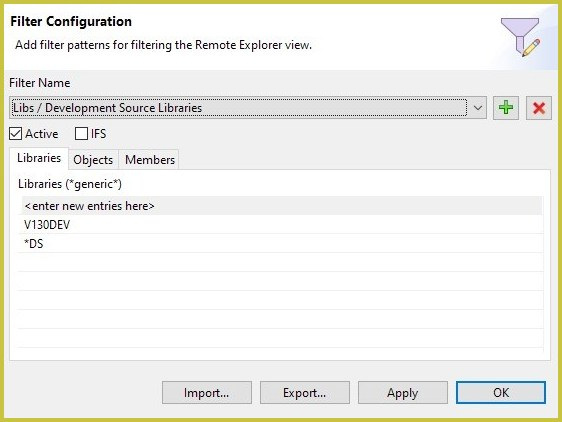
Explorer Filters
Filters come in very handy in order to restrict the number of visible items in the remote explorer. Once a filter is created, it can be activated and de-activated from the drop-down menu. If no filters are active, all items (libraries, objects, directories and files) will be visible. If a filter is active, then only the items selected by the filter will be visible. Creating and configuring filters with MiWorkplace is very easy, and you can stack many of them so that you can quickly hide or show items.
Editing Files
Editing sources is the main goal of any IDE. MiWorkplace is not different.
After you have created a connection, you can find any file and double-click it to open the editor. Depending on the file’s extension (language), there’s additional support beyond just editing text, from syntax coloring to code completion.
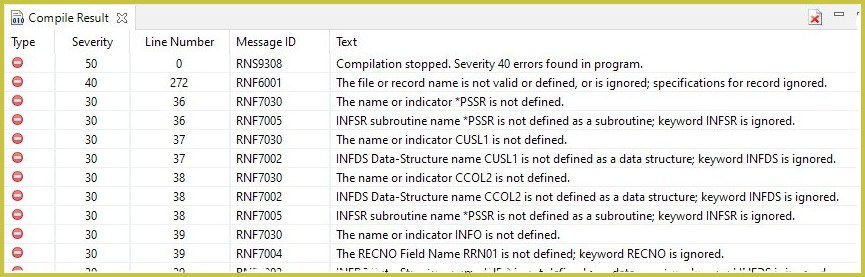
Compiling
The editor cannot compile the source code by itself, but supports starting a compilation of the source code on the server. The compilation can be started via the main menu, with a keyboard shortcut, or from the Remote Explorer, via the context menu of a source member. The parameters or options for the compile command can be set globally and for each member separately. A static text can be passed as compile options but the editor also supports placeholders or variables. The result of a compilation will be automatically fetched from the server and displayed in the Compile Result view, like the image shows.
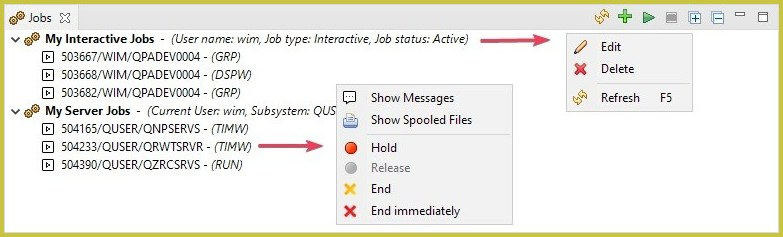
Working with jobs
Jobs on IBM i are an essential part of the development lifecycle, and they are integrated into MiWorkplace. The editor enables you to:
- Create one or more filters to list specific jobs.
- Interact with the job.
- Show the job log messages in a way aimed at quick troubleshooting.
- Show the spooled files of the job.

Spooled files
The editor can manage and show spooled files. The view Spooled Files lists the spooled files of the connection associated with the current selection in the Remote Explorer view. Initially, the view will only show your spooled files.
The available actions are:
- Open spooled file in an extra view (read only).
- Hold (do not print) the spooled file.
- Release after Hold (make ready for printing).
- Copy to another output queue.
- Move to another output queue.
- Delete.
Other features include
- Object properties listing.
- Default source editor.
- Sources can be stored in source members and stream files.
- Local history.
- RPG, CL, DDS and markdown editors.
- Templates and Snippets.
- IBM i System Debugger integration.
- ILEDocs documentation generation and direct upload.
- User defined actions.
- Internal Script Editor.
- REST UI.
- And more.
New Features On V1.25.0
- Integration with TD/OMS.
- Flexible filtering system.
- IFS selection.
- Enhanced Job View.
- Switch to toggle between the IFS and QSys objects.
- Add multiple libraries to a connection.
- Quickly search ‘previous’ and ‘next’.
- A shortcut to decrease/increase font size.
- And more.
CONTACT US
Get in Touch!
FAQ
What is regression testing?
Regression testing (rarely, non-regression testing) is re-running functional and non-functional tests to ensure that previously developed and tested software still performs as expected after a change. If not, that would be called a regression.
What is end-to-end testing?
End-to-end testing is a software testing methodology that verifies the behavior and functionality of an entire application or system from start to finish. It focuses on testing the flow of data and processes across various components, subsystems, and interfaces, ensuring that the system works as intended and meets the desired requirements. In end-to-end testing, the system is tested as a whole, simulating real-world scenarios and user interactions to validate its functionality, performance, and reliability. It involves testing multiple interconnected modules or components to ensure seamless integration and proper functioning of the complete system.
Why is it often difficult to test an IBM i interactive application with 5250 screens?
Traditional 5250 screens are text-based and lack well-defined user interface elements. This can make it challenging to automate the testing process using conventional UI automation tools. Interacting with 5250 screens often requires emulating terminal input and capturing text-based output, which is automatically provided with our tool.
What is the ROI of testing in a digital transformation project?
The return on investment (ROI) of testing in a digital transformation project can be substantial. While the exact ROI will vary depending on the project and organization, here are several ways testing can contribute to ROI: Early Issue Identification and Cost Reduction: Testing helps identify defects, bugs, or functional gaps early in the development process. By catching and addressing issues early, organizations can avoid costly rework, minimize the impact on downstream processes, and reduce the overall project costs. Improved Customer Experience: Digital transformation projects often aim to enhance the customer experience. Through thorough testing, organizations can ensure that the transformed systems, applications, or interfaces provide a seamless, user-friendly experience. This can result in increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and potentially higher revenue generation. Reduced Downtime and Business Disruptions: Effective testing minimizes the risk of system failures, downtime, or disruptions during the transformation or after the go-live. By identifying and addressing potential issues in advance, organizations can avoid business interruptions, maintain operational continuity, and prevent revenue loss. Enhanced System Performance and Scalability: Performance testing and load testing activities help identify and address performance bottlenecks, scalability issues, or potential limitations of the transformed system. Ensuring that the system can handle increased workloads or user demands improves overall system performance, user satisfaction, and the organization’s ability to handle growth. Compliance and Risk Mitigation: Digital transformation projects often involve compliance with industry regulations, security standards, and data privacy requirements. Effective testing ensures that the transformed system meets these compliance needs, minimizing the risk of regulatory penalties, reputational damage, or legal issues. Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Thorough testing helps identify areas for process improvement, automation opportunities, or usability enhancements. By streamlining workflows, eliminating manual tasks, and improving system efficiency, organizations can realize productivity gains, cost savings, and improved employee satisfaction. Reduced Maintenance and Support Costs: Proper testing helps identify and rectify issues before the system goes into production. This can lead to a decrease in post-production support and maintenance costs as fewer defects or issues arise, resulting in improved system stability and reduced ongoing support efforts. It’s important to note that the ROI of testing in a digital transformation project is influenced by various factors, such as the project’s scale, complexity, industry, and the effectiveness of the testing processes implemented. Organizations should consider these factors when planning and allocating resources for testing, aiming to maximize the ROI and ensure the successful outcome of the transformation project.


